Nutrition care for patients after digestive surgery is one of the critical factors determining the speed of recovery and long-term health. After surgery, the digestive system is often weakened and requires time to adapt and restore its function. Choosing and preparing the right types of food can help patients recover quickly and avoid unwanted complications.
Why is nutrition important after digestive surgery?
Post-surgery, the body needs a substantial supply of nutrients to regenerate tissues, strengthen the immune system, and recover health. Additionally, digestion becomes more challenging during this period, especially for patients who have undergone major surgeries such as gastrectomy, duodenectomy, or bowel resection. An improper diet can lead to severe consequences like malnutrition, infections, or delayed wound healing.

Nutritional principles for patients after digestive surgery
Here are some essential principles when designing a diet for patients after digestive surgery:
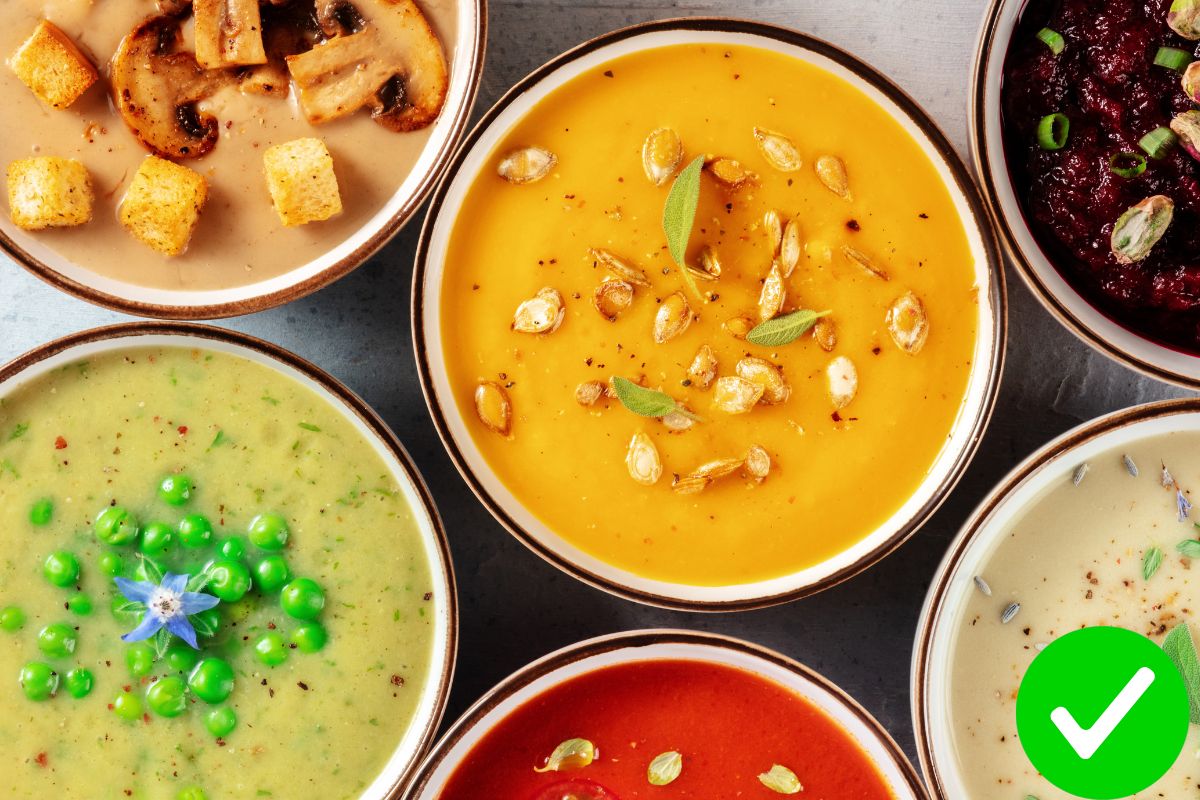
- Soft, easily digestible foods: In the early days post-surgery, patients can typically only consume liquid or soft foods that are easy for the digestive system to process. Popular options include porridge, soups, juices, and smoothies.
- Small, frequent meals: The stomach and intestines may not be able to handle large amounts of food at once. Dividing meals into 5-6 smaller portions daily reduces the digestive burden while ensuring sufficient nutrient intake.
- Protein- and vitamin-rich foods: Protein is essential for cell regeneration and wound healing. Foods like chicken, fish, eggs, and beans are rich protein sources. Additionally, vitamins and minerals from vegetables and fruits boost the immune system.
- Reduce fat, salt, and sugar: Foods high in oil, salt, and sugar can cause discomfort and slow down digestion. Limiting these types of food helps the digestive system work more efficiently and prevents complications such as bloating or diarrhea.
Nutritional phases after surgery
The recovery process after digestive surgery is typically divided into different phases, each requiring a specific dietary approach to best support the body.
- Initial phase (1-3 days post-surgery): During this stage, patients are often limited to drinking water, clear broths, or fiber-free juices. This helps cleanse the digestive system and avoids stressing the stomach and intestines.
- Transition phase (4-7 days post-surgery): As the body begins to adapt, patients can consume soft and liquid foods like thin porridge, milk, and soups. Foods high in fat and fiber should still be avoided as they are harder to digest.
- Recovery phase (after 7 days): Once the digestive system starts to stabilize, patients can gradually return to a normal diet. However, it’s essential to continue prioritizing easily digestible and nutrient-rich foods such as lean meats, leafy greens, and low-fat dairy products.
Foods to eat and avoid after surgery
To aid recovery, patients should focus on the following types of food:
Recommended:
- Lean meats, fish, and eggs to provide protein.
- Soft-cooked vegetables that are easy to digest.
- Low-fat yogurt and cheese for calcium and protein.
- Whole grains that are rich in fiber but easy to digest.
Avoid:
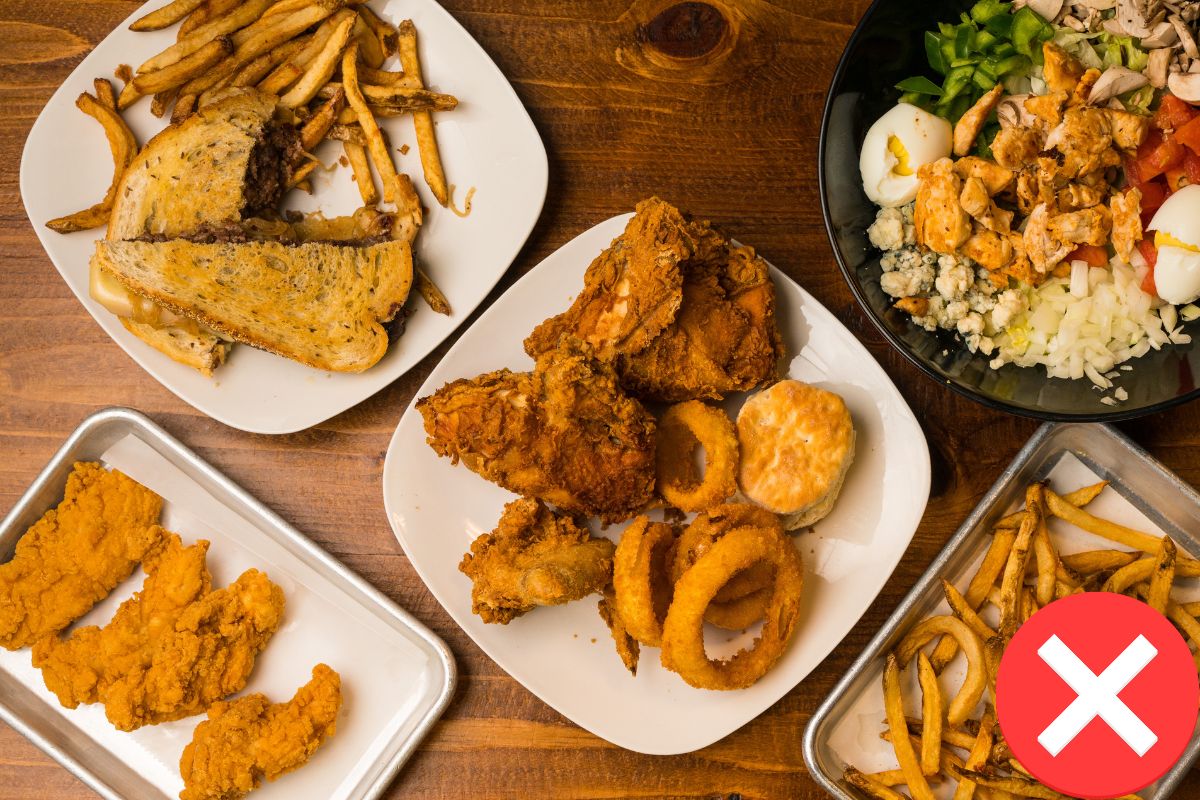
- Fried or greasy foods that are difficult to digest.
- Spicy or hot foods that can irritate the stomach and intestines.
- High-fiber raw vegetables and hard fruits that are not fully cooked.
- Carbonated drinks, coffee, and alcoholic beverages.
Adjusting food textures for patients
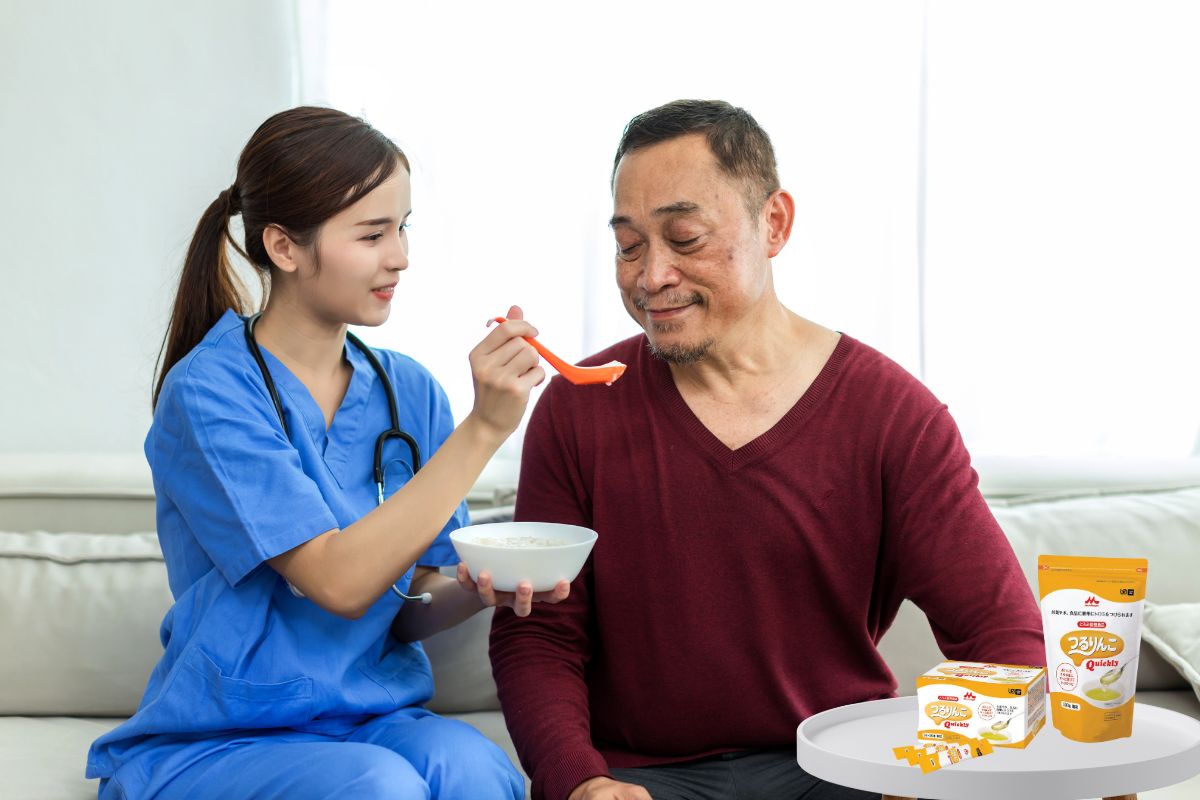
A common issue after digestive surgery is difficulty swallowing or digesting food, especially in elderly patients. In these cases, supportive products like Morinaga Tsururinko can help adjust the texture of food while retaining its nutritional value, making it easier for patients to consume. This product is designed to soften and modify the consistency of food without affecting its taste, making it ideal for those requiring a soft or liquid diet.
The importance of maintaining long-term nutritional balance
While careful eating is crucial during the initial post-surgery phase, maintaining a healthy and balanced diet in the long term is equally important. To ensure stable health and avoid long-term complications like malnutrition or disease recurrence, patients should continue with proper dietary habits that provide adequate protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Additionally, engaging in light and regular physical activities after recovery can enhance overall health and help the digestive system function more effectively.
In summary, nutrition plays an essential role in ensuring a swift and effective recovery after digestive surgery. By choosing appropriate foods, adjusting preparation methods, and maintaining nutritional balance, patients can not only improve their immediate health but also ensure long-term well-being. Using supportive products like Morinaga Tsururinko can facilitate better eating habits, but the most critical aspect is listening to the body and adhering to medical advice.


 Vietnamese
Vietnamese  日本語
日本語  English
English 






